EDRMM: enhancing drug recommendation via multi-granularity and multi-attribute representation (EDRMM:通过多粒度和多属性表示增强药物推荐)
- 数据简介:
期刊:BMC Bioinformatics
卷期/文章号:26(1): 173(2025)
DOI:10.1186/s12859-025-06167-4
作者: Feiyan Liu, Wenhao Wang, Jiawei Zheng, Yibo Xie, Xiaoli Wang, Dongxiang Zhang
英文摘要:
Drug recommendation is a crucial application of artificial intelligence in medical practice. Although many models have been proposed to solve this task, two challenges remain unresolved: (i) most existing models use all historical visits as input, overlooking fine-grained correlations between historical and current information; (ii) Electronic Health Records (EHRs) are underutilized, with only partial information considered to describe patient conditions. To tackle the challenges, we propose a novel drug recommendation model, denoted by EDRMM, which incorporates multi-granularity and multi-attribute information into representation learning. We develop a longitudinal attribute-level history selection mechanism to effectively identify fine-grained historical information that is highly relevant to a patient’s current clinical conditions. We analyze the impact of key Electronic Health Record (EHR) attributes, demonstrating that incorporating such attributes into patient representations can further boost performance. We also design an adaptive global Drug–Drug Interaction (DDI) risk regularization term for the DDI loss function to better balance accuracy and safety during training.
中文摘要:
药物推荐是人工智能在医疗实践中的重要应用。尽管已有许多模型被提出来解决这一问题,但仍存在两个挑战:(i) 大多数现有模型使用所有历史就诊记录作为输入,忽略了历史信息与当前信息之间的细粒度关联;(ii) 电子健康记录 (EHR) 未得到充分利用,仅考虑了部分信息来描述患者病情。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种新的药物推荐模型,记为 EDRMM,该模型将多粒度和多属性信息融入到表征学习中。我们开发了一种纵向属性级历史选择机制,以有效识别与患者当前临床状况高度相关的细粒度历史信息。我们分析了关键电子健康记录 (EHR) 属性的影响,表明将这些属性融入患者表征中可以进一步提升性能。我们还为 DDI 损失函数设计了一个自适应全局药物相互作用 (DDI) 风险正则化项,以更好地平衡训练过程中的准确性和安全性。
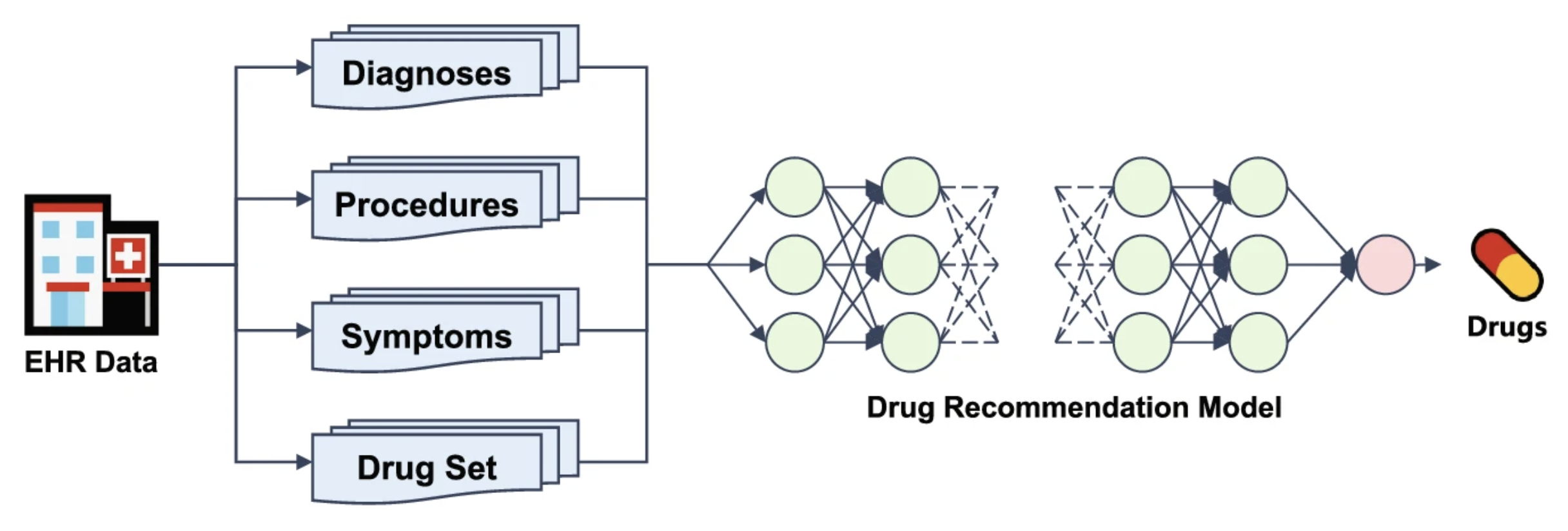
图一 EDRMM 架构图
