SEACC: Self-evolving and adaptive contrastive learning for classification of pediatric pneumonia and AP/PA chest radiographs. (SEACC:用于儿童肺炎和胸部正位/后前位X光片分类的自演化和自适应对比学习)
- 数据简介:
期刊: Displays
论文页码: 81: 102607
DOI: 10.1016/j.displa.2023.102607
作者: , , , , , ,
英文摘要:
Accurate diagnosing of pneumonia and recognizing Anteroposterior and Posteroanterior in pediatric patients through chest X-ray (CXR) are critical components of contemporary computer-aided medical imaging systems. However, a prevalent issue in current methodologies is the suboptimal representation due to class imbalance, which is particularly pronounced in medical images, given the limited quantitative data for certain classes. Furthermore, despite the promising performance of deep learning models, they often face challenges when confronted with various manifestations of pediatric pneumonia and other lung diseases, aside from pneumonia itself. Thus, enhancing model generalization becomes imperative. To address these limitations, this paper presents a novel approach that combines weight adaptive contrast learning and knowledge governor distillation, namely SEACC. Firstly, we employ self-knowledge distillation, leveraging sample-level soft targets to enhance the model’s generalization without incurring additional computational overhead. Secondly, we incorporate supervised contrastive learning, introducing innovative contrast weights among positive samples based on feature similarity. This technique promotes feature representations that exhibit intra-class compactness and inter-class dispersion. Experimental evaluations are conducted on a publicly Guangzhou Women and Children’s Medical dataset, showing an improvement in Recall by 3.3, in AUC by 10.1, surpassing the existing SOTA methods.
中文摘要:
通过胸部X光片(CXR)准确诊断儿童肺炎并识别前后位和后前位是现代计算机辅助医学成像系统的关键组成部分。然而,当前方法普遍存在一个问题,即由于类别不平衡导致的表征欠佳,这在医学图像中尤为突出,因为某些类别的定量数据有限。此外,尽管深度学习模型表现出色,但在面对儿童肺炎和其他肺部疾病(除肺炎本身外)的各种表现时,它们常常面临挑战。因此,提高模型的泛化能力势在必行。为了解决这些局限性,本文提出了一种结合权重自适应对比学习和知识蒸馏的新方法,即SEACC。首先,我们采用自知识蒸馏,利用样本级软目标来增强模型的泛化能力,而无需增加额外的计算开销。其次,我们引入监督对比学习,基于特征相似性在正样本之间引入创新的对比权重。该技术促进了类内紧凑性和类间分散性兼具的特征表示。在公开的广州妇幼保健数据集上进行了实验评估,结果表明召回率提高了3.3%,AUC提高了10.1,优于现有最先进的方法。
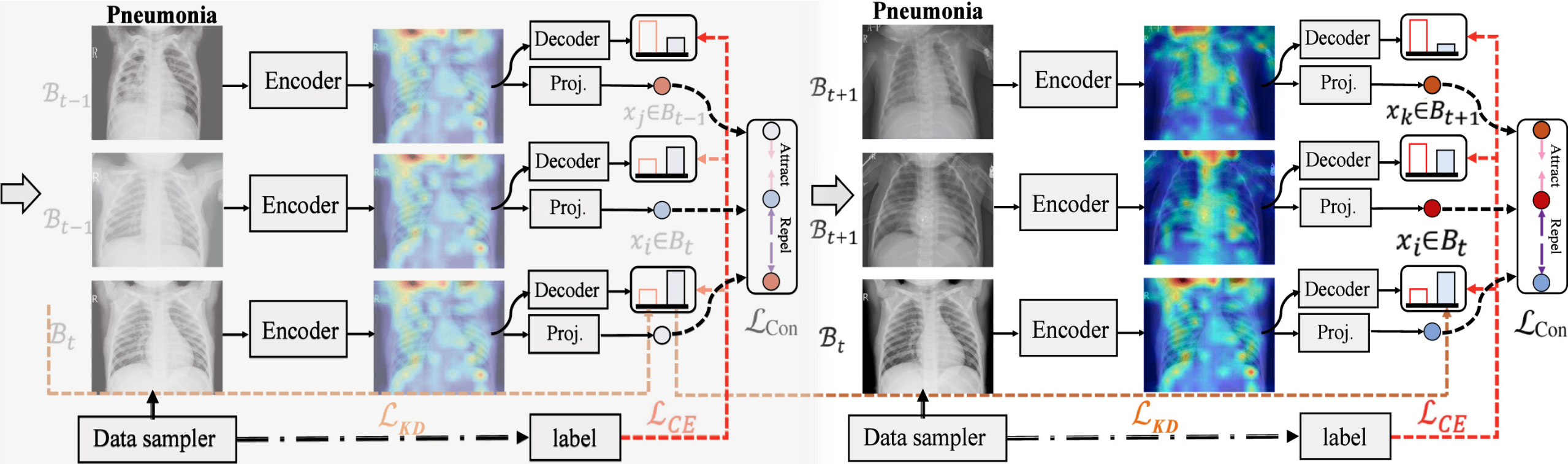
图一 SEACC架构
