Promoting appropriate medication use by leveraging medical big data. (利用医疗大数据促进合理用药)
- 数据简介:
期刊: Frontiers in Digital Health
论文页码: 6: 1198904
DOI: 10.3389/fdgth.2024.1198904
作者: Linghong Hong; Shiwang Huang; Xiaohai Cai; Zhiming Lin; Yunting Shao; Longbiao Chen; Min Zhao; Chenhui Yang
英文摘要:
According to World Health Organization statistics, inappropriate medication has become an important factor affecting the safety of rational medication. In the gray area of medical insurance supervision, such as designated drugstores and medical institutions, there are lots of inappropriate medication phenomena regarding “big prescription for minor ailments.” A traditional clinical decision support system is mostly based on established rules to regulate inappropriate prescriptions, which are not suitable for clinical environments and require intelligent review. In this study, we model the complex relationships between patients, diseases, and drugs based on medical big data to promote appropriate medication use. More specifically, we first construct the medication knowledge graph based on the historical prescription big data of tertiary hospitals and medical text data. Second, based on the medication knowledge graph, we employ a Gaussian mixture model to group patient population representation as physiological features. For diagnostic features, we employ pre-training word vector Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers to enhance the semantic representation between diagnoses. In addition, to reduce adverse drug interactions caused by drug combinations, we employ a graph convolution network to transform drug interaction information into drug interaction features. Finally, we employ the sequence generation model to learn the complex relationships between patients, diseases, and drugs and provide an appropriate medication evaluation for doctor prescriptions in small hospitals from two aspects: drug list and medication course of treatment. In this study, we utilize the MIMIC III dataset alongside data from a tertiary hospital in Fujian Province to validate our model. The results show that our method is more effective than other baseline methods in the accuracy of the medication regimen prediction of rational medication. In addition, it achieved high accuracy in the appropriate medication detection of prescription in small hospitals.
中文摘要:
根据世界卫生组织的统计,不合理用药已成为影响合理用药安全性的重要因素。在医保监管的灰色地带,例如指定药店和医疗机构,存在大量“小病大药”的不合理用药现象。传统的临床决策支持系统大多基于既定规则来规范不合理用药,但这并不适用于临床环境,需要进行智能审核。本研究基于医疗大数据,构建了患者、疾病和药物之间复杂的关联模型,以促进合理用药。具体而言,我们首先基于三级医院的历史处方大数据和医疗文本数据构建了药物知识图谱。其次,基于该药物知识图谱,我们采用高斯混合模型将患者群体特征分组为生理特征。对于诊断特征,我们采用基于Transformer的预训练词向量双向编码器表示(BiENR)来增强诊断之间的语义表示。此外,为了减少药物组合引起的不良反应,我们采用图卷积网络将药物相互作用信息转化为药物相互作用特征。最后,我们采用序列生成模型来学习患者、疾病和药物之间的复杂关系,并从药物清单和治疗疗程两个方面对小型医院的医生处方进行合理的用药评估。本研究利用MIMIC III数据集以及福建省某三级医院的数据来验证我们的模型。结果表明,我们的方法在合理用药方案预测的准确性方面优于其他基线方法。此外,该方法在小型医院处方用药合理性检测方面也取得了较高的准确率。
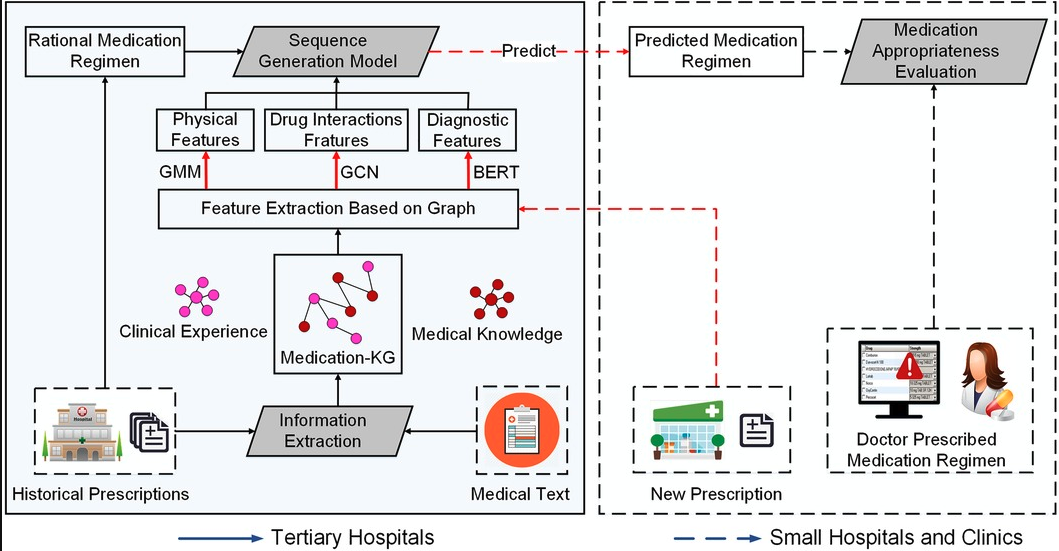
图一 工作架构
